Associated production of amylases and cellulases through submerged fermentation
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.14295/vetor.v34i1.15874Keywords:
Enzyme production, bioprocesses, bacteria, Hydrolytic enzymesAbstract
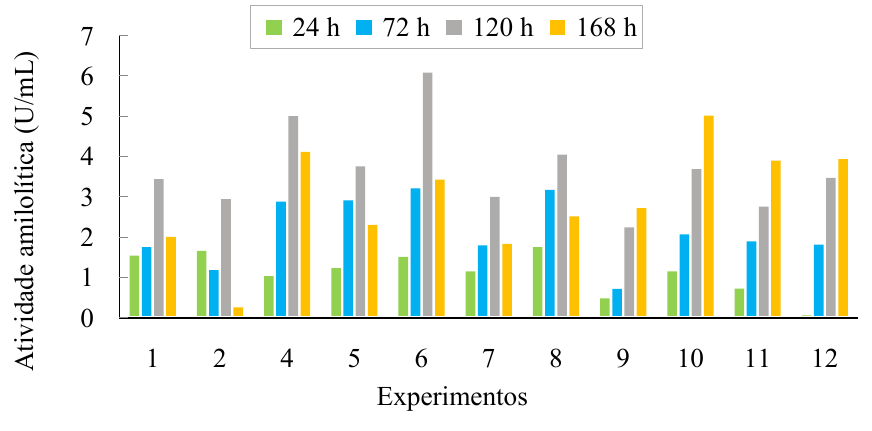
The study aims to optimize the homemade production of amylolytic and cellulolytic enzymes by submerged fermentation. Enzyme production was carried out using sugarcane bagasse and triticale flour as substrates for the fermentation medium, using bacteria isolated from agro-industrial residues. Enzymatic extracts were evaluated for amylolytic and cellulolytic activity. The significant variables (p<0.05) in the amylolytic production were the bacteria and the nitrogen source, for cellulolytic production the bacteria, the nitrogen concentration, and the source. Furthermore, the maximum enzymatic activities were obtained at 120h for both studied enzymes. In this sense, fermentation could be ended in 120 h due to the high production of the enzymes of interest (6.02 U/mL for amylolytic activity and 5.52 U/mL for cellulolytic activity). A second submerged fermentation was carried out, fixing the variables that did not show significance according to the Plackett-Burman design and evaluating two concentrations of ammonium sulfate (0.25 and 0.50%). Enzyme production by bacteria A and B showed no statistical difference (p>0.05) between the experiments, demonstrating that using 0.25% ammonium sulfate is preferable. This allowed for determining the optimized conditions for producing and combining bacterial amylases and cellulases at home, using Bacteria B in a culture medium supplemented with 0.25% ammonium sulfate as the nitrogen source.
Downloads
References
A. Jukola, “Enzyme recovery with microfiltration: effect of spacer size and improvement of membrane cleaning,” Dissertação de Mestrado, School of Engineering Sciences: Chemical Processes R&D, Lappeenranta University of Technology, Finlândia, 2018. Disponível em: https://lutpub.lut.fi/handle/10024/158662
T. Oliveira, “Avaliação Da Produção De Enzimas Celulolíticas Por Fungos Isolados Da Região Dos Campos Gerais”, Dissertação de mestrado, Programa de Pós-Graduação em Biotecnologia, Universidade Tecnológica Federal do Paraná, Ponta Grossa, Brasil, 2020. Disponível em: http://riut.utfpr.edu.br/jspui/handle/1/23800
K. C. Lee, W. Y. Tong, D. Ibrahim, T. Arai, Y. Murata, Y. Mori, e A. Kosugi , “Evaluation of Enzymatic Deinking of Non-impact Ink Laser-Printed Paper Using Crude Enzyme from Penicillium rolfsii c3-2(1) IBRL,” Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, vol. 181, pp. 451–463, 2017. Disponível em: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-016-2223-4
B. Danso, S. S. Ali, R. Xie, e J. Sun, “Valorisation of wheat straw and bioethanol production by a novel xylanase- and cellulase-producing Streptomyces strain isolated from the wood-feeding termite, Microcerotermes species,” Fuel, vol. 310, pp. 122333, 2022. Disponível em: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2021.122333
A. Sidar, E. D. Albuquerque, G. P. Voshol, A. F. J. Ram, E. Vijgenboom, e P. J. Punt, “Carbohydrate Binding Modules: Diversity of Domain Architecture in Amylases and Cellulases From Filamentous Microorganisms,” Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, vol. 8, 2020. Disponível em: https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2020.00871
S. Kiran, S. Kumari, A. Singh, C. Prabha, e S. Kumari, “Extracelluar amylase production under submerged fermentation by Bacillus Subtilis RK6,” International Journal of Pharmacy and Biological Sciences, vol. 8, no. 1, pp. 376-383, 2018. Disponível em: https://www.ijpbs.com/ijpbsadmin/upload/ijpbs_5ad6e1390b158.pdf
A. A. Al Mousa, A. M. A. Hassane, A. E.-R. F. Gomaa, J. A. Aljuriss, N. D. Dahmash, e N. F. Abo-Dahab, “Response-Surface Statistical Optimization of Submerged Fermentation for Pectinase and Cellulase Production by Mucor circinelloides and M. hiemalis,” Fermentation, vol. 8, no 5, pp. 205, 2022. Disponível em: https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8050205
J. G. W. Siqueira, C. Rodrigues, L. P. de S. Vandenberghe, A. L. Woiciechowski, e C. R. Soccol, “Current advances in on-site cellulase production and application on lignocellulosic biomass conversion to biofuels: A review,” Biomass and Bioenergy, vol. 132, pp. 105419, 2020. Disponível em: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2019.105419
Z. Su, J. Luo, X. Li, e M. Pinelo, “Enzyme membrane reactors for production of oligosaccharides: A review on the interdependence between enzyme reaction and membrane separation,” Separation and Purification Technology, vol. 243, pp. 116840, 2020. Disponível em: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2020.116840
S. Saldarriaga-Hernández et al., “Biotransformation of lignocellulosic biomass into industrially relevant products with the aid of fungi-derived lignocellulolytic enzymes,” International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, vol. 161, pp. 1099–1116, 2020. Disponível em: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.06.047
A. Singh, S. Bajar, A. Devi, e D. Pant, “An overview on the recent developments in fungal cellulase production and their industrial applications,” Bioresource Technology Reports, vol. 14, pp. 100652, 2021. Disponível em: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biteb.2021.100652
P. Leite, D. Sousa, H. Fernandes, M. Ferreira, A. R. Costa, D. Filipe, M. Gonçalves, H. Peres, I. Belo, e J. M. Salgado,, “Recent advances in production of lignocellulolytic enzymes by solid-state fermentation of agro-industrial wastes,” Current Opinion in Green and Sustainable Chemistry, vol. 27, pp. 100407, 2021. Disponível em: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cogsc.2020.100407
L. F. Rojas, P. Zapata, e L. Ruiz-Tirado, “Agro-industrial waste enzymes: Perspectives in circular economy,” Current Opinion in Green and Sustainable Chemistry, vol. 34, pp. 100585, 2022, Disponível em: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cogsc.2021.100585
E. F. Rodrigues, “Produção e purificação de enzimas amilolíticas para hidrólise enzimática de biomassa de Spirulina,” Dissertação de mestrado, Programa de Pós-Graduação em Ciência e Tecnologia de Alimentos, Universidade de Passo Fundo, Passo Fundo, Brasil, 2016. Disponível em: http://tede.upf.br:8080/jspui/handle/tede/1350
G. H. Hansen, M. Lübeck, J. C. Frisvad, P. S. Lübeck, e B. Andersen, “Production of cellulolytic enzymes from ascomycetes: Comparison of solid state and submerged fermentation,” Process Biochemistry, vol. 50, no. 9, pp. 1327–1341, 2015. Disponível em: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2015.05.017
J. Liu , J. Yang, R. Wang, L. Liu, Y. Zhang, H. Bao, J. M. Jang, E. Wang, e H. Yuan, “Comparative characterization of extracellular enzymes secreted by Phanerochaete chrysosporium during solid-state and submerged fermentation,” International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, vol. 152, pp. 288–294, 2020. Disponível em: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.02.256
D. G. L. Lemos, “Utilização de bagaço de malte da indústria cervejeira para produção de amilase por amostras de Aspergillus spp. isolados de amostras do solo da Caatinga de Pernambuco,” Dissertação de Mestrado, Programa de Pós-Graduação em Desenvolvimento em Processos Ambientais, Universidade Católica de Pernambuco, Recife, 2021. Disponível em: http://tede2.unicap.br:8080/handle/tede/1481
R. Sirohi, A. Singh, A. Tarafdar, N. C. Shahi, A. K. Verma, e A. Kushwaha, “Cellulase Production from Pre-treated Pea Hulls Using Trichoderma reesei Under Submerged Fermentation”, Waste Biomass Valorization, vol. 10, no. 9, pp. 2651–2659, 2019. Disponível em: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-018-0271-4
S. Bajar, A. Singh, e N. R. Bishnoi, “Exploration of low-cost agro-industrial waste substrate for cellulase and xylanase production using Aspergillus heteromorphus,” Applied Water Science, vol. 10, no. 6, pp. 153, 2020. Disponível em: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-020-01236-w
G. Janarny e K. D. P. P. Gunathilake, “Changes in rice bran bioactives, their bioactivity, bioaccessibility and bioavailability with solid-state fermentation by Rhizopus oryzae,” Biocatalysis and Agricultural Biotechnology, vol. 23, pp. 101510, 2020. Disponível em: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2020.101510
P. Dhaver, B. Pletschke, B. Sithole, e R. Govinden, “Isolation, screening, preliminary optimisation and characterisation of thermostable xylanase production under submerged fermentation by fungi in Durban, South Africa,” Mycology, vol. 13, no. 4, pp. 271–292, 2022. Disponível em: https://doi.org/10.1080/21501203.2022.2079745
B. C. Aita, S. S. Spannemberg, S. Schmaltz, G. L. Zabot, M. V. Tres, R. C. Kuhn, e M. A. Mazutt, “Production of cell-wall degrading enzymes by solid-state fermentation using agroindustrial residues as substrates,” Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, vol. 7, no. 3, pp. 103193, 2019. Disponível em: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2019.103193
J. D. Pejin, L. V. Mojović, D. J. Pejin, S. D. Kocić-Tanackov, D. S. Savić, S. B. Nikolić, e A. P. Djukić-Vuković, “Bioethanol production from triticale by simultaneous saccharification and fermentation with magnesium or calcium ions addition,” Fuel, vol. 142, pp. 58–64, 2015. Disponível em: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2014.10.077
A. Hemati, M. Nazari, B. Asgari Lajayer, D. L. Smith, e T. Astatkie, “Lignocellulosics in plant cell wall and their potential biological degradation,” Folia Microbiol (Praha), vol. 67, no. 5, pp. 671–681. 2022, Disponível em: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-022-00974-5
G. L. Miller, “Use of Dinitrosalicylic Acid Reagent for Determination of Reducing Sugar,” Analytical Chemistry, vol. 31, no. 3, pp. 426–428, 1959. Disponível em: https://doi.org/10.1021/ac60147a030
A. Rempel, T. Machado, H. Treichel, E. Colla, A. C. Margarites, e L. M. Colla, “Saccharification of Spirulina platensis biomass using free and immobilized amylolytic enzymes,” Bioresource Technology, vol. 263, pp. 163–171, 2018. Disponível em: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.04.114
A. S. Qureshi, I. Khushk, C. H. Ali, Y. Chisti, A. Ahmad, e H. Majeed, “Coproduction of protease and amylase by thermophilic Bacillus sp. BBXS-2 using open solid-state fermentation of lignocellulosic biomass”, Biocatalysis and Agricultural Biotechnology, vol. 8, pp. 146–151, 2016. Disponível em: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2016.09.006
A. L. C. C. Simões, “Produção de Amilases dor Cultivo em Estado Sólido e Hidrólise Enzimática de Resíduos de Mandioca”, Dissertação de Mestrado, Programa de Pós-Graduação em Engenharia Química, Universidade Federal da Paraíba, João Pessoa, Brasil, 2021. Disponível em: https://repositorio.ufpb.br/jspui/handle/123456789/21944
R. J. B. Devos, “Produção de enzimas e bioetanol a partir de matérias-primas amiláceas e resíduos de hortifruti”, Dissertação de Mestrado, Programa de Pós-Graduação em Ciência e Tecnologia de Alimentos, Universidade de Passo Fundo, Passo Fundo, Brasil, 2022. Disponível em: http://tede.upf.br:8080/jspui/handle/tede/2204
C. Mori, A. J. Nascimento, e M. Z. Miranda, “Aspectos econômicos e conjunturais da cultura de triticale no mundo e no Brasil.”, Passo Fundo: Embrapa Trigo, 2014. Disponível em: http://www.cnpt.embrapa.br/biblio/do/p_do150.htm (acessado em 22 de agosto de 2023).
M. A. Farooq, S. Ali, A. Hassan, H. M. Tahir, S. Mumtaz, e S. Mumtaz, “Biosynthesis and industrial applications of α-amylase: a review”, Archives of Microbiology, vol. 203, no 4, pp. 1281–1292, 2021, Disponível em: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-020-02128-y
F. A. Santos, L. C. T. Carvalho-Gonçalves, A. L. C. Cardoso-Simões, e S. F. M. Santos, “Evaluation of the production of cellulases by Penicillium sp. FSDE15 using corncob and wheat bran as substrates”, Bioresource Technology Reports, vol. 14, pp. 100648, 2021. Disponível em: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biteb.2021.100648
E. M. Penha, L. A. N. Viana, L. M. F. Gottschalk, S. C. Terzi, E. F. Souza, S. C. Freitas, J. O. Santos, e T. F. C. Salum, “Aproveitamento de resíduos da agroindústria do óleo de dendê para a produção de lipase por Aspergillus niger”, Ciência Rural, vol. 46, no 4, pp. 755–761, 2015. Disponível em: https://doi.org/10.1590/0103-8478cr20131673
J. Furhan, N. Salaria, M. Jabeen, e J. Qadri, “Partial purification and characterisation of cold-active metalloprotease by Bacillus sp. Ap1 from apharwat peak, kashmir”, Pakistan Journal of Biotechnology, vol. 16, no. 1, pp. 47–54, 2019. Disponível em: https://pjbt.org/index.php/pjbt/article/view/48
P. Biswas, A. K. Bharti, A. Kadam, e D. Dutt, “Wheat bran as substrate for enzyme production and its application in the bio-deinking of mixed office waste (MOW) paper”, Bioresources, vol. 14, no 3, pp. 5788–5806, 2019. Disponível em: https://doi.org/10.15376/biores.14.3.5788-5806
O. C. Amadi, E. J. Egong, T. N. Nwagu, G. Okpala, C. O. Onwosi, G. C. Chukwu, B. N. Okolo, R. C. Agu, e A. N. Moneke, “Process optimization for simultaneous production of cellulase, xylanase and ligninase by Saccharomyces cerevisiae SCPW 17 under solid state fermentation using Box-Behnken experimental design”, Heliyon, vol. 6, no 7, pp. e04566, 2020. Disponível em: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e04566
V. M. Vasconcellos, P. W. Tardioli, R. L. C. Giordano, e C. S. Farinas, “Production efficiency versus thermostability of (hemi)cellulolytic enzymatic cocktails from different cultivation systems”, Process Biochemistry, vol. 50, no 11, pp. 1701–1709, 2015. Disponível em: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2015.07.011
N. Srivastava, A. Mohammad, R. Singh, M. Srivastava, A. Syed, D. B. Pal, A. M. Elgorban, P. K. Mishra, e V. K. Gupta, “Evaluation of enhanced production of cellulose deconstructing enzyme using natural and alkali pretreated sugar cane bagasse under the influence of graphene oxide”, Bioresource Technology, vol. 342, pp. 126015, 2021, Disponível em: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2021.126015